Distribution of mercury and organic matter in particle-size classes in sediments contaminated by a waste water treatment plant: Vidy Bay, Lake Geneva, Switzerland
Abstract
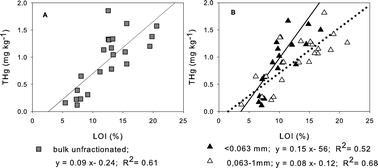
In Lake Geneva, Switzerland, the most Hg-contaminated sediments have been found in the Vidy Bay where high Hg contents largely exceeds the background levels of Lake Geneva sediments. This contamination has been attributed to the discharge of a waste water treatment plant (WWTP). Total Hg (THg) and monomethylmercury (MMHg) were determined in bulk sediment and in three different grain size fractions (i: clay and silt, ii: fine-coarse sand, iii: and very coarse sand and gravel) collected close to the outlet pipe of a WWTP in order to verify whether the standardized procedures of sediment treatment is adequate for this setting and, by extension, for similar contaminated sites. THg was homogeneously distributed in the different grain size fractions and was correlated to organic matter content (R2 = 0.6). MMHg was homogeneously distributed in the two finer grain fractions (Φ < 0.063 mm; 0.063 mm < Φ <1 mm). The results of this study suggested that the analysis of the bulk sediment seems to be more appropriate for the assessment of the content and spatial distribution of Hg in freshwater sediments contaminated by WWTPs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...