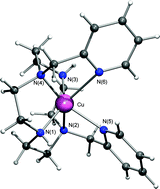
The synthesis of the cross-bridged cyclen CRpy2 {4,10-bis((pyridin-2-yl)methyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazabicyclo[5.5.2]tetradecane}, a constrained analogue of the previously described trans-methylpyridine cyclen Cpy2 is reported. The additional ethylene bridge confers to CRpy2proton-sponge type behaviour which was explored by NMR and potentiometric studies. Transition metal complexes have been synthesized (by complexation of both ligands with Co2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+) and characterized in solution and in the solid state. The single crystal X-ray structures of [CoCpy2]2+, [CuCpy2]2+ and [ZnCpy2]2+ complexes were determined. Stability constants of the complexes, including those of the cross-bridged derivative, were determined using potentiometric titration data and the kinetic inertness of the [CuCRpy2]2+ complex in an acidic medium (half-life values) was evaluated by spectrophotometry. The pre-organized structure of the cross-bridged ligand imposes an additional strain for the complexation leading to complexes with smaller thermodynamic stability in comparison with the related non-bridged ligand. The electrochemical study involving cyclic voltammetry underlines the importance of the ethylene cross-bridge on the redox properties of the transition metal complexes.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...