Size-dependent catalytic activity and geometries of size-selected Pt clusters on TiO2(110) surfaces
Abstract
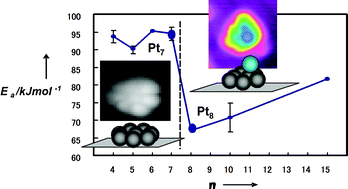
Scanning tunneling microscope observations show a geometrical transition from a planar structure to a 3D structure at n = 8. This geometrical transition resulted in a significant decrease in the activation energy of the CO oxidation reaction. The upper-layer Pt atoms of the 3D cluster structure that starts to form at n = 8 are low-coordinated Pt atoms, and they may play an important role in the CO oxidation reaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...