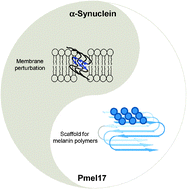
Amyloid has been traditionally viewed in the context of disease. However, the emerging concept of ‘functional amyloid’ has taken a new direction into how we view amyloid. Recent studies have identified amyloid fibrils ranging from bacteria to humans that have a beneficial role, instead of being associated with a misfolded state that has been implicated in diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and prion diseases. Here, we review our work on two human amyloidogenic polypeptides, one associated with Parkinson’s disease, α-synuclein (α-syn), and the other important for melanin synthesis, the repeat domain (RPT) from Pmel17. Particularly, we focused our attention on spectroscopic studies of protein conformation and dynamics and their impact on α-syn amyloid formation and for RPT, we discussed the strict pH dependence of amyloid formation and its role in melanin biosynthesis.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...