Weak interactions in ion–ligand complexes of C3H +3 isomers: competition between H-bound and C-bound structures in c-C3H +3·L and H2CCCH+·L (L = Ne, Ar, N2, CO2, and O2)†
Abstract
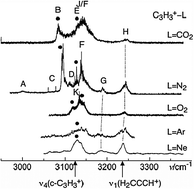
Explicitly correlated coupled cluster theory at the CCSD(T)-F12x level (T. B. Adler, G. Knizia, and H.-J. Werner, J. Chem. Phys.127, 221106, 2007) has been employed to study structures and vibrations of complexes of type c-C3H+3·L and H2C3H+·L (L = Ne, Ar, N2, CO2, and O2). Both
- This article is part of the themed collection: Weak hydrogen bonds – strong effects?
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...