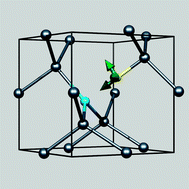
The low mass of hydrogen leads to highly localised, high-frequency vibrational modes associated with H-containing defects in crystalline materials. In addition to vibrational spectroscopy, the presence of hydrogen in diamond has been identified from several experimental techniques. In particular, paramagnetic resonance shows that H is often associated with lattice vacancies, but in many cases the microscopic structure of the defects remains to be determined. We present the results of first-principles density-functional modelling of selected H-containing point defects, reporting both the calculated frequencies and the change in frequencies with applied strain. We show that more constrained environments lead to significantly larger strain-related shifts in frequency than more open environments, such as where the H is associated with lattice vacancies.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...