Enhanced reactivity of Pt nanoparticles supported on ceria thin films during ethylenedehydrogenation
Abstract
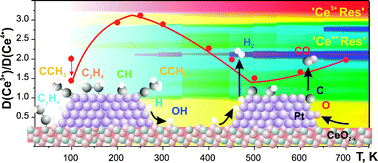
The
* Corresponding authors
a
Lehrstuhl für Physikalische Chemie II, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Egerlandstraße 3, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
E-mail:
yaroslava.lykhach@chemie.uni-erlangen.de
Fax: +49 9131 8528867
Tel: +49 9131 8520944
b Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Department of Plasma and Surface Science, V Holešovičkách 2, 18000 Prague 8, Czech Republic
c Sincrotrone Trieste, Strada Statale 14, km 163.5, 34149 Basovizza-Trieste, Italy
d Erlangen Catalysis Resource Center, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Egerlandstraße 3, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
The

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Y. Lykhach, T. Staudt, N. Tsud, T. Skála, K. C. Prince, V. Matolín and J. Libuda, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011, 13, 253 DOI: 10.1039/C0CP00345J
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
