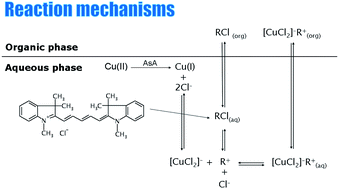
A reaction based on ion associate formation between dimethylindodicarbocyanine polymethine dye 1,3,3-trimethyl-2-[5-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydroindol-2-ylidene)-penta-1,3-dienyl]-3H-indolium (DIDC) and Cu(I) in the presence of chloride ions as ligand is used to develop a liquid–liquid extraction procedure for the separation and preconcentration of copper with subsequent graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometric detection. The optimum reaction conditions for ion associate formation and extraction were found to be: pH 3–5, 0.24–0.36 mol L−1 of chloride, 0.05–0.12 mmol L−1 of DIDC, amyl acetate as extraction solvent, an aqueous to organic phase ratio of 5 : 1 mL : mL. A linear response was obtained in the range 0.4–4.8 μg L−1 of Cu, and the limit of detection, calculated from a regression equation based on three times the standard deviation of the blank, was 0.10 μg L−1. The method was applied to the determination of Cu in real samples. It is important to note that the presented method can also be applied to the determination of Cu(I) in the presence of a 125-fold excess of Cu(II), thus enabling the speciation analysis.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...