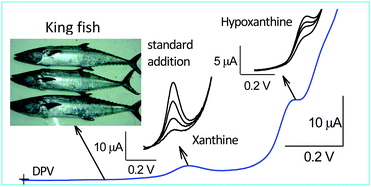
A simple electrochemical sensor was designed, based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with “as commercially received” multiwalled carbon nanotubes (GCE/MWCNT), for the simultaneous detection of three purine bases: uric acid (UA), xanthine (X) and hypoxanthine (Hx) by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). Comparison amongst various carbon nanotubesviz.; as commercially received-MWCNT, functionalized-MWCNT, purified-MWCNT and single walled carbon nanotubes for modified electrode preparation, and in turn for the simultaneous electrochemical detection of the purines by DPV, the “as received MWCNT” modified GCE showed the best performance in terms of well-separated peaks and higher peak current values. Scan rate experiments on discreet oxidations of UA, X and Hx suggested that the electron-transfer mechanism for both UA and X follows a mixed diffusion–adsorption controlled pathway, while in the case of Hx, a diffusion controlled route is followed. Calibration responses for the simultaneous detection of UA, X and Hx were linear up to 700, 200 and 150 μM respectively. Corresponding detection limit values were 141 nM, 134 nM and 2.87 μM. Finally analysis of UA, X and Hx content in three different fresh dead fish samples was successfully demonstrated with recoveries of around 100%.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...