Micellar mediated trace level mercury quantification through the rhodamine B hydrazide spirolactam ring opening process
Abstract
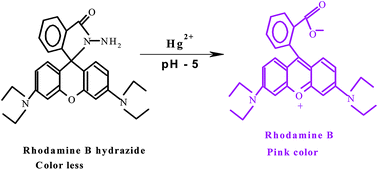
The micellar mediated trace level estimation of mercury in industrial effluent sample by the rhodamine B hydrazide spirolactam ring opening process is described. The catalytic reaction of mercuric ion with colorless rhodamine B

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...