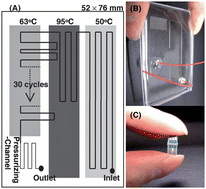
Rapid and definitive diagnosis is critical to the prevention of the spread of endemic human pathogenic viruses. Detection of variant specific genes by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) has become a routine diagnostic test for accurate subtyping of RNA viruses, such as influenza. In this paper, we demonstrate the use of a continuous-flow polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microfluidic RT-PCR chip and disposable electrical printed (DEP) chips for rapid amplification and sensing of new influenza (AH1pdm) virus of swine-origin. The RT-PCR chip consisted of four zones: RT reaction zone, initial denaturation zone, thermal cycle zone for PCR (2-step PCR) and pressurizing-channel zone for preventing air-bubble formation. In order to measure electrochemical signals, methylene blue (MB), an electro-active DNA intercalator, was added to the RT-PCR mixture. The RT-PCR was completed within 15 min which was the total flow-through time from the inlet to the outlet, and the reduction signals from amplifications could be detected quickly on the DEP chip. The MB reduction current on the DEP chip with the amplicon significantly reduced compared to non-amplified controls. This microfluidic platform for rapid RT-PCR and the DEP chip for quick electrochemical sensing are suitable for integration, and have the potential to be a portable system for diagnostic tests.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...