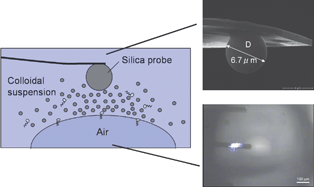
This study contributes to the understanding of the effects of confining surface properties on the interactions within thin liquid films of colloidal nanoparticles. Colloidal probe atomic force microscopy was used for studying the interaction of colloidal nanoparticles between the solid–liquid and air–liquid interfaces. The influence of the surfactant on the surface deformability and on the structuring of the nanoparticles was determined. Therefore, surfactants of different charges, i.e.sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (C16TAB) and β-dodecylmaltoside (β-C12G2) were chosen. The oscillatory force caused by the layering formation of the nanoparticles was detected between the AFM microsphere probe and the bubble, and the oscillatory wavelength that reflected the interlayer distance of the nanoparticles was found to scale with colloidal nanoparticle concentration as c−1/3. Under constant experimental conditions (AFM probe radius, bubble size, Debye length and contact angle), the bubble stiffness was found to increase linearly with surface tension, while the oscillatory wavelength was not affected by the bubble’s deformability. In addition, the cationic surfactant C16TAB displayed different behavior on the retraction part of the force curve, in which a pronounced adhesion force was observed. This phenomenon might be attributed to the hydrophobization caused by the monolayer formation of cationic surfactant on the silica sphere surface. Thus a stable thin film of colloidal nanoparticles was assumed to be formed between the silica microsphere and the bubble when electrostatic repulsion existed.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...