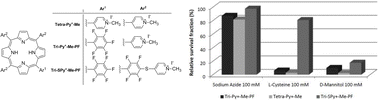
Photodynamic therapy is a very promising approach to inactivate pathogenic microorganisms. The photodamage of cells involves reactive oxygen species (ROS) which are generated in situ by two main mechanisms (type I and/or type II). The mechanism responsible for the photoinactivation (PI) of a bioluminescent recombinant Escherichia coli, induced by three different cationic porphyrins, was identified in this work using a rapid method based on the monitoring of the metabolic activity of this bacterium. The inhibitory effect of the photodynamic process in the presence of a singlet oxygen quencher (sodium azide) or free radical scavengers (D-mannitol and L-cysteine) was evaluated by exposing bacterial suspensions with 0.5 μM Tri-Py+-Me-PF, 5.0 μM Tetra-Py+-Me or 5.0 μM Tri-SPy+-Me-PF to white light. Strong bacterial protection was observed with sodium azide (100 mM) for the three cationic porphyrins. However, in the presence of Tri-Py+-Me-PF and Tetra-Py+-Me and the free radical scavengers (L-cysteine and D-mannitol) the reduction on the bacterial bioluminescence was significantly higher and similar to that obtained in their absence (5.4–6.0 log reduction). In the case of Tri-SPy+-Me-PF two distinct behaviours were observed when L-cysteine and D-mannitol were used as free radical scavengers: while the presence of L-cysteine (100 mM) lead to a bacterial protection similar to the one observed with sodium azide, in the presence of D-mannitol only a small protection was detected. The high inhibition of the PS activity by L-cysteine is not due to its radical scavenger ability but due to the singlet oxygen quenching by the sulfanyl group (–SH). In fact, the photodecomposition of 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran in the presence of Tri-SPy+-Me-PF is completely suppressed when L-cysteine is present. The results obtained in this study suggest that singlet oxygen (type II mechanism) plays a very important role over free radicals (type I mechanism) on the PI process of the bioluminescent E. coli by Tri-Py+-Me-PF, Tetra-Py+-Me and Tri-SPy+-Me-PF. Although the use of scavengers is an adequate and simple approach to evaluate the relative importance of the two pathways, it is important to choose scavengers which do not interfere in both PI mechanisms. Sodium azide and D-mannitol seem to be good oxygen and free radical quenchers, respectively, to study the PI mechanisms by porphyrinic photosensitizers.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...