Potent “Clicked” MMP2 Inhibitors: Synthesis, Molecular Modeling and Biological Exploration†
Abstract
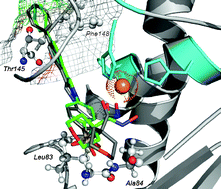
A new series of MMP2
* Corresponding authors
a
Departamento de Química, Facultad de Farmacia, Universidad San Pablo CEU, Urbanización Montepríncipe, Boadilla del Monte, Madrid, Spain
E-mail:
aramgon@ceu.es, bpaster@ceu.es
Fax: (+34)913510496
Tel: (+34)913724796
b Center for Biomedical Research of La Rioja (CIBIR) C/Piqueras 98, Logroño, Spain
c Department of Molecular Biology, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, The John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin, Lublin, Poland
d Structural Biology Laboratory, Medicinal Chemistry Department, Centro de Investigación Príncipe Felipe, Avda. Autopista del Saler, 16, Valencia, Spain
A new series of MMP2

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
J. M. Zapico, P. Serra, J. García-Sanmartín, K. Filipiak, R. J. Carbajo, A. K. Schott, A. Pineda-Lucena, A. Martínez, S. Martín-Santamaría, B. de Pascual-Teresa and A. Ramos, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2011, 9, 4587 DOI: 10.1039/C0OB00852D
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
