Comparison of two- and three-dimensional activity landscape representations for different compound data sets
Abstract
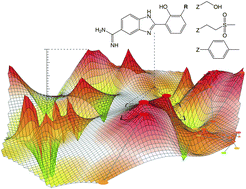
Modeling of activity landscapes provides a basis for the analysis of structure–activity relationships (SARs) in large compound data sets. Activity landscape models enable visual access to SAR features. Regardless of their specific details, these models generally have in common that they integrate molecular similarity and potency relationships between active compounds. Different two-dimensional (2D) landscape representations have been introduced and recently also the first detailed three-dimensional (3D) model. Herein we compare advanced 2D and 3D activity landscape models for compound data sets having different SAR character. Although the compared 2D and 3D representations are conceptually distinct, it is found that global SAR features of compound data sets can be equally well deduced from them. However, local SAR information is often captured in different ways by these representations. Since these 2D and 3D landscape modeling tools have been made freely available, the analysis also provides guidelines for how to best utilize these alternative landscape representations for practical SAR analysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...