Inverted organic photovoltaic devices with high efficiency and stability based on metal oxide charge extraction layers
Abstract
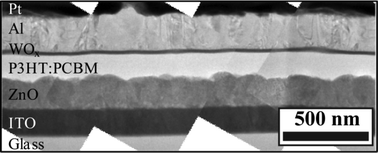
A substantial increase in device performance and operational stability in solution processed inverted bulk heterojunction (BHJ) organic photovoltaic devices (OPV) is demonstrated by introducing a zinc oxide (ZnO) interlayer between the electron collecting bottom

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...