A robust, particle size independent, method for quantifying metal(loid oxide) nanoparticles and their agglomerates in complex environmental matrices by electrothermal vaporisation coupled to ICP-MS†
Abstract
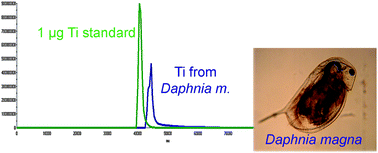
The demand to quantify the elemental composition of very small sample amounts and/or of samples which form artefacts during conventional sample preparations is increasing. Example applications are the quantification of engineered metal(loid) based nanomaterials in environmental samples, e.g. (i) the direct analyses of engineered
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...