Electrospun mats of PVP/ACP nanofibres for remineralization of enamel tooth surfaces†
Abstract
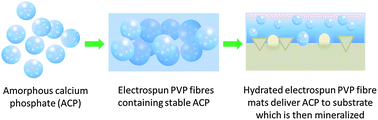
The inorganic component of dental hard tissues consists of crystalline hydroxyapatite (HAP) and has been the focus of extensive studies in biomineralization. Dental enamel is exposed to constant demineralization and remineralization within the oral environment, and an imbalance between these processes can result in the conditions of dental erosion or dentine hypersensitivity, or both. This study demonstrates the novel use of electrospun mats of amorphous

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...