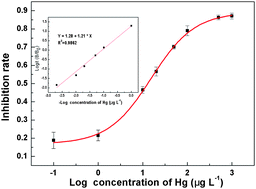
A competitive indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was developed and successfully applied in a dissolved mercury assay. For mercury quantification, factors including the concentration of chelator EDTA, pH, ionic strength, and blocking solution were optimized in this study. Generally the detection limit of the ELISA was standardized as 0.459 μg L−1, with an IC50 value of 13.09 μg L−1 and linear range of 1 to 500 μg L−1; whereas a cross-reactivity study showed that the immunoassay was quite specific for mercury, compared with nine other metal ions. The recovery of the method was evaluated by spiking ultrapure water, tap water and surface water of Taihu Lake with mercury at 1, 10, 50, 100 μg L−1. The precision of the method was evaluated by spiking ultrapure water with mercury at 1, 10, 50, and 100, 500 and 1000 μg L−1. The coefficients of variation of intra- and inter-assay were below 10% in most cases, and recoveries were 94.3–123.5%, 91.9–117.9%, and 92.3–115.6% for ultrapure water, tap water and surface water of Taihu Lake, respectively. Therefore, the developed method is able to determine mercury at levels below the maximum residue limits of water quality standards for drinking water sources of China.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...