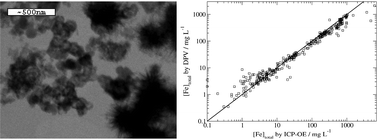
A voltammetric procedure for the determination of total, dissolved, solid phase and nanoparticulate Fe in polluted mine-waters has been developed. Mine-water samples were collected from abandoned mine sites in the UK, which have been designated by the UK Coal Authority for remediation research and for routine monitoring of mine-water quality. Monthly samples were taken over the period March, 2006 to April, 2007 from six different sites in North East England. The samples were analysed directly using differential pulse voltammetry at gold electrodes: separate peaks due to unhydrolysed and hydrolysed Fe aquo ions could be assigned and quantified. The results show that our analysis provides data for total dissolved iron of comparable analytical quality to the established mine-water analysis techniques based on inductively-coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy. Further, the difference between differential pulse voltammetry data in acidified and unacidified samples allows quantitation of the Fe-containing solid phase and nanoparticulate Fe oxyhydroxide phases. If samples were pre-filtered, then these measurements also allowed us to determine the fraction of Fe present in nanoparticles <450 nm diameter. Finally, steady-state voltammetry at Pt microelectrodes was used to obtain the ratio of Fe(II) and Fe(III) redox states in the soluble Fe fraction.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...