An artificially constructed direct Z-scheme heterojunction: WO3 nanoparticle decorated ZnIn2S4 for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production†
Abstract
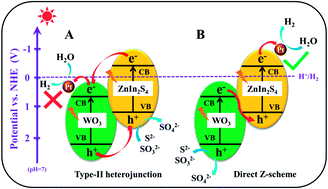
Photocatalytic H2 evolution has been proven as one of the promising strategies for addressing global energy and environmental issues. Herein, a binary Z-scheme heterostructure of a WO3/ZnIn2S4 photocatalyst was artificially constructed through a simple hydrothermal method. A variety of characterization tests were employed to prove the effective coupling of WO3 nanoparticles and ZnIn2S4 particles for the fabrication of the WO3/ZnIn2S4 heterostructure. It was found that the decoration of WO3 nanoparticles could significantly promote the photocatalytic H2 evolution activity of ZnIn2S4 under visible-light irradiation, and the H2 evolution rate of 5 wt% WO3/ZnIn2S4 composite could reach 1945.88 μmol h−1 g−1, which was 7.9 times that of pristine ZnIn2S4 and could rival that of previously reported ZnIn2S4-based photocatalysts. On the basis of photoelectrochemical results, the direct Z-scheme heterojunction rather than the type-II heterojunction was proposed to explain the significantly enhanced photocatalytic performance of the WO3/ZnIn2S4 photocatalyst. The enhancement of photocatalytic activity could be attributed to the efficient Z-direction charge transfer at the WO3/ZnIn2S4 heterostructure interface, thus reducing the recombination rate of the photogenerated carriers of the system. This work provides new insights into the construction of direct Z-scheme heterostructured ZnIn2S4-based photocatalysts for highly efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...