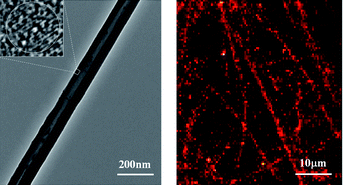
Building additional functionality into self-assembled organic tubes is of great interest for materials and biological applications. Here we report the synthesis and characterization of fluorescent composite tubes in which in situ formed cadmium sulfide (CdS) nanoparticles are embedded in lithocholic acid (LCA) tube walls. The LCA/CdS composite tubes are characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) absorption spectroscopy, and confocal fluorescence microscopy. The reported data show that the fluorescence of the composite tubes stems from CdS nanoparticles with the cubic (zinc blende) crystal structure that are embedded in the tube walls. As the fluorescence of CdS nanocrystals is bright, easily distinguishable, and resistant to photobleaching, long-term fluorescence microscopy observation of these LCA tubes is feasible. In addition, the shape of the fluorescent composite tubes can be controlled by the pH of the aqueous solution in which the tubes are formed. At pH 9.5, the self-assembled composite tubes show a straight shape, while at pH 13.0 the self-assembled composite tubes coil into a left-handed helix. The fluorescent composite tubes with pH-controlled shapes are a promising system for a variety of materials and biological applications.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...