Biocatalytic carboxylation†
Abstract
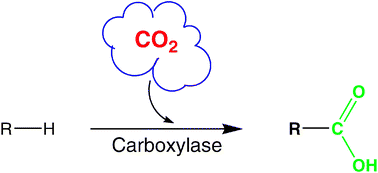
Dwindling petroleum feedstocks and increased CO2-concentrations in the atmosphere currently open the concept of using CO2 as raw material for the synthesis of well-defined organic compounds. In parallel to recent advances in the chemical CO2-fixation, enzymatic (biocatalytic)

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...