Interfacial layers of stimuli-responsive poly-(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylicacid) (PNIPAM-co-MAA) microgels characterized by interfacial rheology and compression isotherms
Abstract
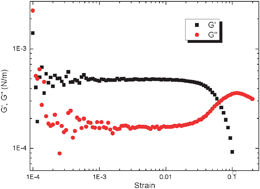
Stimuli-sensitive emulsions stabilized by microgel particles consisting of poly-(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylicacid) (PNIPAM-co-MAA) and being responsive to both pH and temperature have been investigated with respect to the visco-elastic properties of the interfacial layer. Properties of the interfacial layer were probed by means of shear and dilatational

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...