Tuning structural forces between silica surfaces by temperature-induced micellization of responsive block copolymers
Abstract
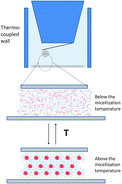
The aim of this study is to demonstrate a method to control interactions between two surfaces by the use of a responsive solution. This was done by performing

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...