Kinetic spectroscopy of heme hydration and ligand binding in myoglobin and isolated hemoglobin chains: an optical window into heme pocket water dynamics
Abstract
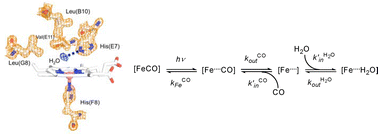
The entry of a
- This article is part of the themed collection: Water in biological systems

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...