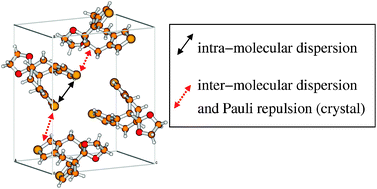
Importance of London dispersion effects for the packing of molecular crystals: a case study for intramolecular stacking in a bis-thiophene derivative
Abstract
The influence of London dispersion effects in density functional theory for the computation of molecular crystals is investigated. The structure of
- This article is part of the themed collection: Solid State Structure Prediction

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...