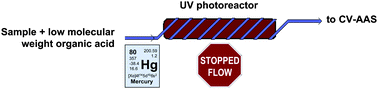
Photo-chemical vapour generation has been applied in a flow-injection system under stopped-flow conditions for determination of Hg by atomic absorption spectrometry. The system allows mercury vapour generation without the need for conventional reduction reactions based on sodium/potassium tetrahydroborate (III) or tin chloride in acid medium. The photo-induced reaction is accomplished by applying ultraviolet irradiation (UV) to the sample solution containing Hg(II) in the presence of an organic acid (i.e., acetic, citric, oxalic, ethylendiaminetetraacetic) as precursor of reducing species. A remarkable improvement in sensitivity is observed with acetic acid when stopped-flow is employed as compared to continuous operation, meaning that kinetics play an important role in the photo-induced reaction. A detection limit of 0.3 μg L−1 can be obtained, which represents a 6-fold improvement in respect to that obtained without stopped-flow. The repeatability expressed as relative standard deviation was about 2.7% (n = 15) for a 50 μg L−1 Hg standard. The effect of potential interferences on the photo-generation of Hg vapour was investigated. In the UV-photo-induced CVG, both inorganic Hg and organomercury species can be reduced to elemental mercury with the same efficiency. The method was applied to determination of Hg in several enriched natural water samples and recoveries of MeHg+, Thiomersal, EtHg+ and PhHg+ were in the range 97% to 102%.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...