Topological transition dynamics in a strained bubble cluster
Abstract
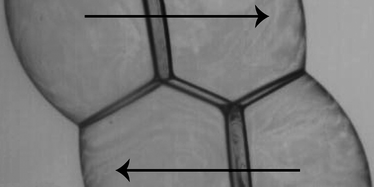
We study experimentally the dynamics of strain-induced T1 neighbour switching in clusters of 3D bubbles. To determine the physico-chemical processes that set the time scale of such rearrangements, foaming solutions of a wide range of well characterized bulk and interfacial rheological properties are used. At low strain rates, the time scale is set by a balance between surface tension and surface viscous forces, and we present a simple physical model that explains these findings, on the basis of previous experimental and theoretical work with 2D foams.1 At higher strain rates, rearrangement dynamics are driven by the applied strain. In a wider context, our study of T1s in bubble clusters provides insight into the structural relaxations that accompany the flow of 3D foams.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...