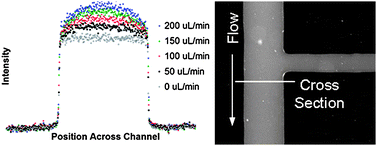
Poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) microchannels are commonly used microfluidic structures that have a wide variety of biological testing applications, including the simulation of blood vessels to study the mechanics of vascular disease. In these studies in particular, the deformation of the channel due to the pressure inside is a critical parameter. We describe a method for using fluorescence microscopy to quantify the deformation of such channels under pressure driven flow. Additionally, the relationship between wall thickness and channel deformation is investigated. PDMS microchannels of varying top wall thickness were created using a soft lithography process. A solution of fluorescent dye is pumped through the channels at constant volume flow rates and illuminated. Pressure and fluorescence intensity are measured at five positions along the length of the channel. Fluorescence measurements are then used to determine deformation, using the linear relationship of dye layer thickness and intensity. A linear relationship between pressure and microchannel deformation is measured. Pressure drops and deformations closely correspond to values predicted by the model in most cases. Additionally, measured pressure drops are found to be up to 35% less than the pressure drop in a rigid-walled channel, and channel wall thickness is found to have an increasing effect as the channel wall thickness decreases.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...