Depleted uranium analysis in blood by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry†
Abstract
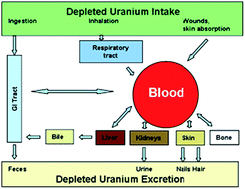
In this study we report depleted uranium (DU) analysis in whole blood samples. Internal exposure to DU causes increased uranium levels as well as change in the uranium isotopic composition in blood specimen. For identification of DU exposure we used the 235U/238U ratio in blood samples, which ranges from 0.00725 for natural uranium to 0.002 for depleted uranium. Uranium quantification and isotopic composition analysis were performed by

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...