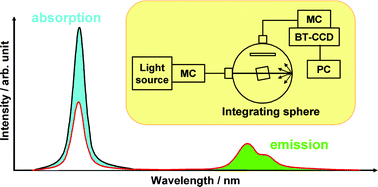
We reevaluate the absolute fluorescence and phosphorescence quantum yields of standard solutions by using a novel instrument developed for measuring the absolute emission quantum yields of solutions. The instrument consists of an integrating sphere equipped with a monochromatized Xe arc lamp as the light source and a multichannel spectrometer. By using a back-thinned CCD (BT-CCD) as the detector, the sensitivity for spectral detection in both the short and long wavelength regions is greatly improved compared with that of an optical detection system that uses a conventional photodetector. Using this instrument, we reevaluate the absolute fluorescence quantum yields (Φf) of some commonly used fluorescence standard solutions by taking into account the effect of reabsorption/reemission. The value of Φf for 5 × 10−3 M quinine bisulfate in 1 N H2SO4 is measured to be 0.52, which is in good agreement with the value (0.508) obtained by Melhuish by using a modified Vavilov method. In contrast, the value of Φf for 1.0 × 10−5 M quinine bisulfate in 1 N H2SO4, which is one of the most commonly used standards in quantum yield measurements based on the relative method, is measured to be 0.60. This value is significantly larger than Melhuish’s value (0.546), which was estimated by extrapolating the value of Φf for 5 × 10−3 M quinine bisulfate solution to infinite dilution using the self-quenching constant. The fluorescence quantum yield of 9,10-diphenylanthracene in cyclohexane is measured to be 0.97. This system can also be used to determine the phosphorescence quantum yields (Φp) of metal complexes that emit phosphorescence in the near-infrared region: the values of Φp for [Ru(bpy)3]2+ (bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine) are estimated to be 0.063 in water and 0.095 in acetonitrile under deaerated conditions at 298 K, while that in aerated water, which is frequently used as a luminescent reference in biological studies, is reevaluated to be 0.040.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...