An update and expansion of our readily applicable structure–activity relationship (SAR) for predicting the barrier height Eb to decomposition by β C–C scission of (substituted) alkoxy radicals is presented. Such alkoxy radicals are key intermediates in the atmospheric oxidation of volatile organic compounds, and a correct description of their chemistry is vital to the understanding of atmospheric chemistry; nevertheless, experimental data on these reactions remain scarce. The SAR is based on quantum chemical characterizations of a large set of alkoxy radicals, and accommodates alkoxy radicals with alkyl- (–R), oxo- (![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), hydroxy- (–OH), hydroperoxy (–OOH), alkoxy (–OR), alkylperoxy- (–OOR), nitroso- (–NO), nitro- (–NO2), nitrosooxy- (–ONO), and nitroxy- (–ONO2) functionalities, as well as 3- to 6-membered rings and some unsaturated side chains. The SAR expresses the barrier height to decomposition, Eb = 17.9 kcal mol−1 + ΣNs×Fs, as a linear function of the number Ns of these substituents on the relevant carbons, and the substituent-specific activities Fs derived from the quantum chemical calculations, allowing facile predictions based solely on the molecular structure. For low barriers, ≤7 kcal mol−1, a simple curvature correction is required. The SAR-predicted barrier height Eb can be used to predict the high-pressure rate coefficient for alkoxy decompositionkdiss at or around 298 K.
O), hydroxy- (–OH), hydroperoxy (–OOH), alkoxy (–OR), alkylperoxy- (–OOR), nitroso- (–NO), nitro- (–NO2), nitrosooxy- (–ONO), and nitroxy- (–ONO2) functionalities, as well as 3- to 6-membered rings and some unsaturated side chains. The SAR expresses the barrier height to decomposition, Eb = 17.9 kcal mol−1 + ΣNs×Fs, as a linear function of the number Ns of these substituents on the relevant carbons, and the substituent-specific activities Fs derived from the quantum chemical calculations, allowing facile predictions based solely on the molecular structure. For low barriers, ≤7 kcal mol−1, a simple curvature correction is required. The SAR-predicted barrier height Eb can be used to predict the high-pressure rate coefficient for alkoxy decompositionkdiss at or around 298 K.
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), hydroxy- (–OH),
O), hydroxy- (–OH), 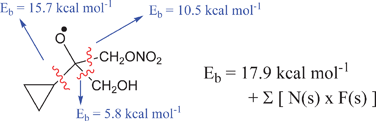

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...