Photophysical comparative study of amylose and polyvinyle pyrrolidone/single walled carbon nanotubes complex
Abstract
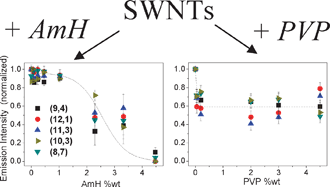
Progressive addition of hydroxypropylated amylose (AmH), from 0.05 wt% to 4.5 wt%, to
* Corresponding authors
a
Institut des Matériaux Jean Rouxel, UMR6502, Université de Nantes-CNRS, 2 rue de la Houssinière, 44322 Nantes cedex 3, France
E-mail:
pierre.m.bonnet@univ-bpclermont.fr
b Laboratoire des Matériaux Inorganiques, UMR6002, Université Blaise Pascal Clermont-Ferrand 2-CNRS, 24 Avenue des Landais, 63177 Aubière cedex, France
c INRA-BIA, site de Nantes, Rue de la Géraudière BP, 71627-44316 Nantes cedex 3, France
Progressive addition of hydroxypropylated amylose (AmH), from 0.05 wt% to 4.5 wt%, to

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
P. Bonnet, J. P. Buisson, N. N. Martyr, H. Bizot, A. Buelon and O. Chauvet, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009, 11, 8626 DOI: 10.1039/B907948C
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
