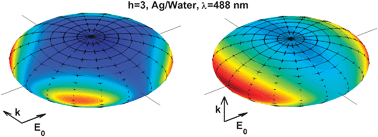
The influence of particle size and shape effects on average and punctual surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) enhancement factors (EFs) is investigated using exact T-matrix electrodynamic calculations of silver and gold spheroids over a large parameter space. This study extends the conventional treatment of these effects within the frameworks of the electrostatics approximation, its generalizations, or Mie theory for spheres. It confirms the qualitative features of these approaches, but provides in addition quantitative predictions of SERS EFs in the case of large non-spherical particles, where the lightning-rod effect (shape effect) and radiation damping (size effect) operate simultaneously. Finally, the localization effect at large SERS EF (hot-spots) is shown to be dictated only by shape, not size, in the case of metallic spheroids at the dipolar localized surface plasmon resonance.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...