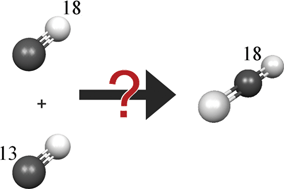
Binary ice mixtures of two carbon monoxide isotopomers, 13C16O and 12C18O, were subjected at 10 K to energetic electrons to investigate the interaction of ionizing radiation with extraterrestrial, carbon monoxide bearing ices. The chemical modifications were monitored on line and in situ via absorption–reflection–absorption Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy as well as in the gas-phase via a quadrupole mass spectrometer. Detected products include two newly formed carbon monoxide isotopomers (12C16O and 13C18O), carbon dioxide (12C16O2, 12C18O16O, 12C18O2, 13C16O2, 13C18O16O, and 13C18O2), and dicarbon monoxide (12C13C16O and 13C13C16O). Kinetic profiles of carbon monoxide and of carbon dioxide were extracted and fit to derive reaction mechanisms and information on the decomposition of carbon monoxide and on the formation of carbon dioxide in extraterrestrial ice analog samples.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...