Ab initio quantum chemical computations of substituent effects on triaziridine strain energy and heat of formation†‡
Abstract
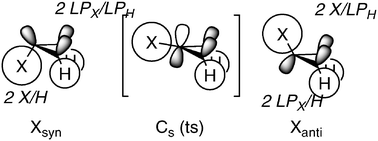
A computational investigation is carried out on the parent triaziridine and as a function of N-substituents. Assessment of heat of formation, ring strain energy, barriers to inversion of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...