Morphology effect on antibacterial activity of cuprous oxide†
Abstract
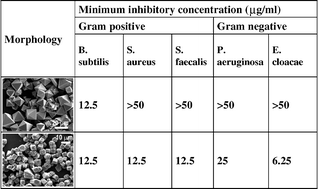
A glycine-mediated mixed-solvothermal approach has been proposed for the synthesis of novel Cu2O structures with different morphologies and the morphology effect on the antibacterial activity of the obtained Cu2O crystals has been studied, confirming that the obtained Cu2O crystals all show good antibacterial effects and that with the morphology of the Cu2O crystals changing from cubic to octahedral, the antibacterial property changes from general bacteriostasis to high selectivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...