Synthesis of stable W/O microemulsions of a hybrid grafted copolymer using a new inorganic cationic backbone within a unique “polyhedral cell”
Abstract
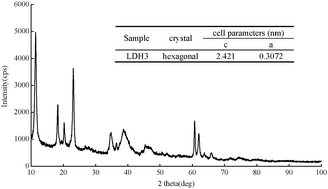
A novel graft copolymerization on an inorganic cationic backbone processing within polyhedral cell(s) (PHC) is discussed. This procedure can produce stabilized W/O (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...