Reactivity of an antimetastatic organometallicruthenium compound with metallothionein-2: relevance to the mechanism of action†
Abstract
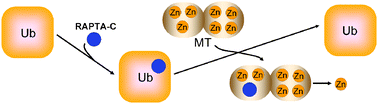
The reaction of metallothionein-2 (MT-2) with the organometallic antitumour compound
* Corresponding authors
a
Institut des Sciences et Ingénierie Chimiques, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), CH-1015 Lausanne, Switzerland
E-mail:
paul.dyson@epfl.ch, angela.casini@epfl.ch
Fax: (+41) 21 6939865
Tel: (P. D.) +41 21 6939854
b Department of Biochemistry, University of Zürich, Winterthurerstrasse 190, CH-8057 Zürich, Switzerland
c Department of Chemistry, University of Florence, Via della Lastruccia 3, 50019 Sesto Fiorentino, Italy
The reaction of metallothionein-2 (MT-2) with the organometallic antitumour compound

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
