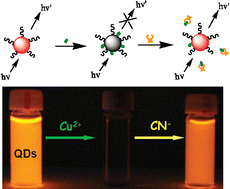
A new fluorescent sensor for the sensitive and selective detection of cyanide (CN−) in aqueous media was developed herein. The sensing approach is based on CN−-modulated quenching behavior of Cu2+ toward the photoluminescence (PL) of CdTe quantum dots (QDs). In the presence of CN−, the PL of QDs that have been quenched by Cu2+ was found to be efficiently recovered, which then allows the detection of CN− in a very simple approach. Experimental results showed that the pH of the buffer solution, concentration of copper ions, and size of CdTe QDs all influenced the response of the sensor to CN−. Under the optimal conditions, a good linear relationship between the PL intensity and the concentration of CN− can be obtained in the range of 3.0 × 10−7 to 1.2 × 10−5 M, with a detection limit as low as 1.5 × 10−7 M. In addition, the present fluorescent sensor possesses remarkable selectivity for cyanide over other anions, and negligible influences were observed on the cyanide detection by the coexistence of other anions or biological species (such as albumin and typical blood constituents). Therefore, we expect the proposed copper ion-modified QDs to be an efficient and reliable sensing system to monitor cyanide concentration in environmental or clinical applications.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...