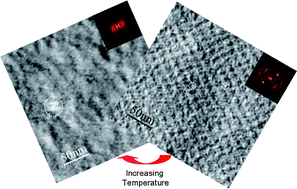
The influence of the temperature on the surface topology, layer thickness and density of recrystallized bacterial S-layers from Bacillus sphaericus CCM2177 on polyelectrolyte multilayers in contact with liquid water was investigated. A quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D) was used to monitor the build-up of the polyelectrolyte multilayer and the adsorption of S-layer protein (1600 ng cm−2). The critical temperature (55 °C) at which the S-layer loses its 2-D structure was obtained from atomic force microscopy (AFM) and confirmed by neutron reflectometry (NR) experiments. The process of S-layer denaturation was found to be irreversible. Aggregates of denatured S-proteins resist lower loads than the crystalline nanostructure formed from folded S-proteins.
The combination of the QCM-D results with the scattering length density and film thickness (14 nm) obtained from neutron reflectometry studies permitted the estimation of the density of adsorbed S-protein together with the bound water (M = 1.16 g cm−3), the dry protein scattering length density (2.02 × 10−6 Å−2) and the S-protein mass density (1.48 g cm−3). The results confirmed that S-proteins form very loosely packed layers on polyelectrolyte multilayers incorporating a water volume fraction of around 68%.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...