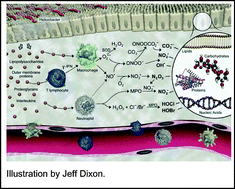
Epidemiological evidence points to a cause and effect relationship between chronic inflammation and human maladies such as cancer, atherosclerosis and autoimmune disease. A critical link between inflammation and disease may lie in the secretion of highly reactive oxygen and nitrogen species by macrophages and neutrophils, including hypohalous acids, nitrous anhydride, and nitrosoperoxycarbonate. Exposure of host epithelial cells to the resulting oxidation, nitration, nitrosation and halogenation chemistries leads to damage of all types of cellular molecules. Since nucleic acids sustain damage representative of the full spectrum of different chemistries and the damage likely plays a causative role in disease etiology, DNA and RNA damage products can serve as surrogates for the short-lived chemical mediators of inflammation, and as markers that provide both mechanistic understanding of the disease process and a means to quantify risk of disease. However, the very small quantities of the damaged molecules pose a challenge to the simultaneous quantification of the spectrum of lesions in the manner of proteomics or metabolomics. The goal of this Highlight is to provide an update on the chemistry of inflammation and the development of biomarkers of inflammation in the age of -omics technologies.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...