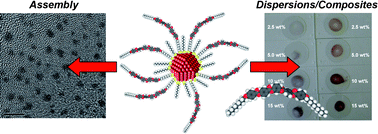
We present the first synthesis of a series of thiol-, thioacetate-, and xanthate-terminated bent-core derivatives, as well as the preparation of gold nanoclusters using the thiol-terminated bent-core compounds. The mesomorphic properties of the bent-core compounds have been investigated by polarizing optical microscopy (POM), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), and electro-optic tests. From this series, the mono-xanthate derivatives form rectangular or hexagonal columnar phases, and the mono-thiol derivative with shorter alkyl chains forms a metastable, likely smectic, phase. All other bent-core compounds and intermediates exclusively form disordered or multi-layer lamellar crystalline solid modifications. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) images of the bent-core functionalized gold nanoclusters prepared from the thiol-terminated derivatives, taken after slow evaporation of the solvent, provide evidence for the formation of self-assembled nanocluster arrays. Upon dispersion of these gold nanoclusters in two structurally related bent-core LC hosts (one forming a SmCPA, and the second with a terminal double bond displaying a Colr phase), a shift in the surface plasmon resonance was observed indicating a LC host-dependent aggregation of the nanoparticles. Finally, we report initial results on the effects of different concentrations of these nanoclusters on the thermal properties as well as the applied voltage/current response of the parent SmCPA host.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...