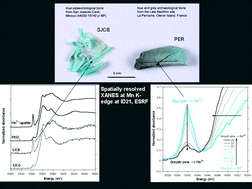
This paper presents new results obtained on coloured palaeontological and archaeological bone and ivory materials by combined microXANES/XRF at Mn K-edge at ID 21 beamline at ESRF. Ancient bone material currently shows blue, grey or black stains which are still an object of much controversy. Recent investigations on blue coloured palaeontological ivory called odontolite used as a semi-precious stone on medieval art objects showed that this material is stained by Mn5+ ions substituted for P5+ in the calcium apatite (Ca5(PO4)3X, X = OH, F, Cl) matrix. As the blue coloration can appear on different palaeontological and archaeological bone material and as the colour is not necessarily homogenous on the specimens, this work shows that the blue coloration of ancient bone material can, generally, be ascribed to the presence of Mn5+ in the bone mineral. It can appear in very different palaeontological and archaeological contexts, also accidentally, and can be considered as a general alteration phenomenon of ancient bone material modified by a heat process. In contrast, the grey and black colour also observed on the same specimens can have different origins, which are, however, generally caused by the presence of Mn oxides or oxyhydroxides. The exact nature of the black Mn compounds depends strongly on the burial context, where the palaeontological and archaeological materials originate from.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...