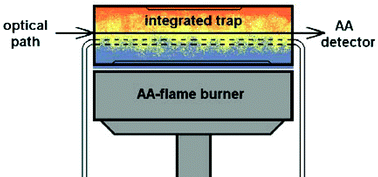
The analytical performance of non-chromatographic coupled hydride generation, integrated atom trap (HG-IAT) atomizer flame absorption spectrometry (FAAS) systems were evaluated for the speciation analysis of antimony in environmental samples. Antimony, using formation of stibine (SbH3) vapors were atomized in an air–acetylene flame-heated IAT. A new design of HG-IAT-FAAS hyphenated technique that would exceed the operational capabilities of existing arrangements (a water-cooled single silica tube, double-slotted quartz tube or an “integrated trap”) was investigated. For the estimation of Sb(III) and Sb(V) concentrations in samples, the difference between the analytical sensitivities of the absorbance signals obtained for antimony hydride without and with previous treatment of samples with L-cysteine can be used. The concentration of Sb(V) was calculated by the difference between total Sbtot and Sb(III). A dramatic improvement in detection limit was achieved compared with that obtained using either of the atom trapping techniques, presented above, separately. This novel approach decreases the detection limit down to low pg mL–1 levels. The concentration detection limit, defined as 3 times the blank standard deviation (3sigma), was 0.2 ng mL–1. For a 120 s in situ pre-concentration time (sample volume of 2 mL), sensitivity enhancement compared to flame AAS, was 550 fold for Sb, using hydride generation-atom trapping technique. The sensitivity can be further improved by increasing the collection time. The precision, expressed by RSD, was 8.0% (n = 6) for Sb. The designs studied include slotted tube, water-cooled single silica tube and integrated atom traps. Reference and real sample materials were analyzed. The accuracy of the method was verified by the use of certified reference materials (NIST SRM 2704 Buffalo River Sediment, SRM 2710 Montana Soil, SRM 1633a Coal Fly Ash, SRM 1575 Pine Needles, SRM 1643e Trace Elements in Water) and by aqueous standard calibration technique (solutions). The measured Sb content, in reference materials, were in satisfactory agreement with the certified values. The hyphenated technique was applied for antimony determinations in soil, sediment, coal fly ash, sewage and river water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...