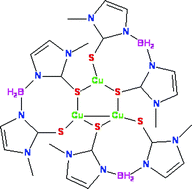
The complexes [Cu(BmMe)]3·0.77C4H8O (1), [(BmMe)Ag(PPh3)] (2) and [M{κ3-H(μ-H)B(tiaz)2}(PPh3)] (M= Cu (3), Ag (4); BmMe = bis(2-mercapto-1-methylimidazolyl)borate, H2B(tiaz)2 = dihydrobis(2-mercaptothiazolyl)borate) have been prepared and characterised by X-ray crystallographic and spectroscopic methods. The presence of M⋯H–B interactions in these species has been investigated using infrared spectroscopy and crystallography. In [Cu(BmMe)]3, the triangular array of three trigonal-planar copper atoms is coordinated by three chelating and bridging (BmMe)− ligands, and has an unusual, highly unsymmetrical arrangement with one short Cu–Cu distance; this is the first structurally authenticated BmMe complex with a nuclearity greater than two. In complexes 2–4, the metal atom is found in a distorted trigonal-planar geometry, bound by a terminal phosphine ligand and two sulfur atoms of a chelating ligand, supplemented by an M⋯H–B interaction, which appears to be a common feature in the coordination chemistry of the (BmMe)− and [H2B(tiaz)2]− ligands; compounds 1–4 are the first reported complexes of copper(I) and silver(I) with any bis(2-mercaptoimidazolyl)borate ligand or with H2B(tiaz)2.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...