The outcome of the reactions of MCl5 (M = Nb, 1a; M = Ta, 1b) with 1,2-dialkoxyalkanes [i.e. MeO(CH2)2OMe (dme), EtO(CH2)2OEt, MeOCH2CH(Me)OMe, MeO(CH2)2OCH2Cl, MeO(CH2)2O(CH2)2OMe (diglyme)] depends strictly on the stoichiometry. In the 1 : 1 molar ratio reactions, single C–O bond cleavage occurs, resulting in formation of alkyl chloride and of the complexes ![[upper bond 1 start]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e010.gif) MCl4[O(R)CH(R′)CH2O]
MCl4[O(R)CH(R′)CH2O]![[upper bond 1 end]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e011.gif) [M = Nb, R = Me, R′ = H, 3a; M = Ta, R = Me, R′ = H, 3b; M = Nb, R = Et, R′ = H, 5; M = Nb, R = R′ = Me, 6; M = Nb, R = CH2Cl, R′ = H, 7; M = Nb, R = (CH2)2O(Me)NbCl5, R′ = H, 8], which have been characterized spectroscopically. Moreover, minor amounts of the oxo-bridged adducts MOCl3(dme)MCl5 (M = Nb, 4a; M = Ta, 4b) have been isolated in the reactions involving dme. On the other hand, compounds 1 react with two (or more) equivalents of dme mainly via a multiple C–O bond cleavage process, affording MOCl3(dme) (M = Nb, 2a; M = Ta, 2b), 1,4-dioxane and methyl chloride. The oxychloride compounds MOCl3 (M = Nb, 11a; M = Ta, 11b) have been efficiently obtained by addition of TiCl4 to 2. Compound 2a is reduced in high yield to the Nb(III) species NbCl3(dme), 12, upon treatment with SnBu3H. The oxychloride NbOCl3(diglyme), 9, 1,4-dioxane, CH3Cl and the hexachloroniobate salt [MeOCH2CH2OCH2CH2O(H)Me][NbCl6], 10, have been identified as products of the reaction of 1a with two equivalents of diglyme. The 1 : 2 molar ratio reaction of 1a with MeOCH2CH(Me)OMe gives 2,5-dimethyl-1,4-dioxane. Compound 1a reacts with two equivalents of EtO(CH2)2OEt or MeO(CH2)2OCH2Cl yielding Cl(CH2)2OCH2CH3 or O(CH2Cl)2 and diglyme, respectively, but not dioxane, suggesting that fragmentation pathways different from that found for dme are operating. The X-ray molecular structures of 4a, 4b and 10 have been determined.
[M = Nb, R = Me, R′ = H, 3a; M = Ta, R = Me, R′ = H, 3b; M = Nb, R = Et, R′ = H, 5; M = Nb, R = R′ = Me, 6; M = Nb, R = CH2Cl, R′ = H, 7; M = Nb, R = (CH2)2O(Me)NbCl5, R′ = H, 8], which have been characterized spectroscopically. Moreover, minor amounts of the oxo-bridged adducts MOCl3(dme)MCl5 (M = Nb, 4a; M = Ta, 4b) have been isolated in the reactions involving dme. On the other hand, compounds 1 react with two (or more) equivalents of dme mainly via a multiple C–O bond cleavage process, affording MOCl3(dme) (M = Nb, 2a; M = Ta, 2b), 1,4-dioxane and methyl chloride. The oxychloride compounds MOCl3 (M = Nb, 11a; M = Ta, 11b) have been efficiently obtained by addition of TiCl4 to 2. Compound 2a is reduced in high yield to the Nb(III) species NbCl3(dme), 12, upon treatment with SnBu3H. The oxychloride NbOCl3(diglyme), 9, 1,4-dioxane, CH3Cl and the hexachloroniobate salt [MeOCH2CH2OCH2CH2O(H)Me][NbCl6], 10, have been identified as products of the reaction of 1a with two equivalents of diglyme. The 1 : 2 molar ratio reaction of 1a with MeOCH2CH(Me)OMe gives 2,5-dimethyl-1,4-dioxane. Compound 1a reacts with two equivalents of EtO(CH2)2OEt or MeO(CH2)2OCH2Cl yielding Cl(CH2)2OCH2CH3 or O(CH2Cl)2 and diglyme, respectively, but not dioxane, suggesting that fragmentation pathways different from that found for dme are operating. The X-ray molecular structures of 4a, 4b and 10 have been determined.
![[upper bond 1 start]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e010.gif) MCl4[O(R)CH(R′)CH2O]
MCl4[O(R)CH(R′)CH2O]![[upper bond 1 end]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e011.gif) [M = Nb, R = Me, R′ = H, 3a; M = Ta, R = Me, R′ = H, 3b; M = Nb, R = Et, R′ = H, 5; M = Nb, R = R′ = Me, 6; M = Nb, R = CH2Cl, R′ = H, 7; M = Nb, R = (CH2)2O(Me)NbCl5, R′ = H, 8], which have been characterized spectroscopically. Moreover, minor amounts of the
[M = Nb, R = Me, R′ = H, 3a; M = Ta, R = Me, R′ = H, 3b; M = Nb, R = Et, R′ = H, 5; M = Nb, R = R′ = Me, 6; M = Nb, R = CH2Cl, R′ = H, 7; M = Nb, R = (CH2)2O(Me)NbCl5, R′ = H, 8], which have been characterized spectroscopically. Moreover, minor amounts of the 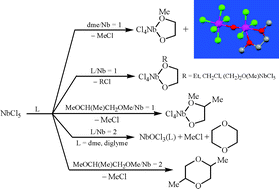

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...