Trapping proton transfer intermediates in the disordered hydrogen-bonded network of cryogenic hydrofluoric acid solutions
Abstract
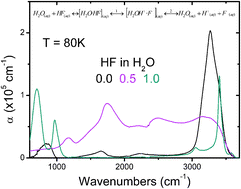
A molecular-level description of the structural and dynamical aspects that are responsible for the weak acid behaviour of dilute hydrofluoric acid solutions and their unusual increased acidity at near equimolar concentrations continues to elude us. We address this problem by reporting reflection–absorption
- This article is part of the themed collection: Water at interfaces
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...