Niobium oxide-supported platinum ultra-low amount electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction†
Abstract
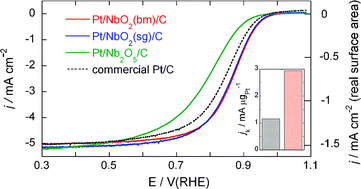
We demonstrate a new approach to synthesizing high-activity electrocatalysts for the O2reduction reaction with ultra low Pt content. The synthesis involves placing a small amount of Pt, the equivalent of a monolayer, on carbon-supported niobium oxide

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...